R语言确实相当的灵活,只要明确数据结构和需求描述,让ai编写代码,就能实现大部分GIS应用的功能。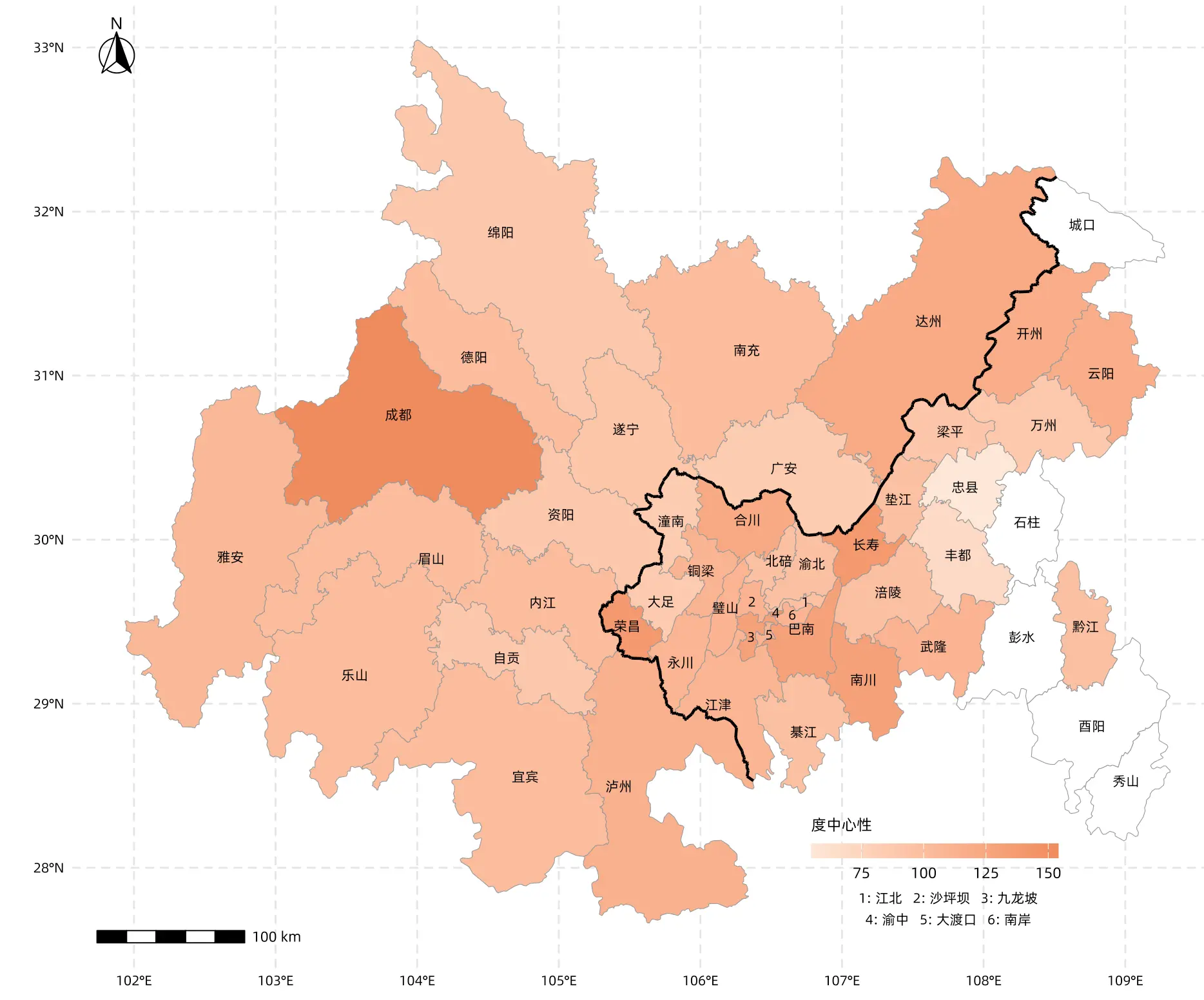
完整代码如下:
# ==============================================================================
# R Script: 成渝双城经济圈社会网络空间分布图
# ==============================================================================
# ---- Step 1: 加载必要的包 ----
library(sf)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(readxl)
library(ggspatial)
library(grid)
library(showtext)
# ---- Step 2: 字体设置 ----
showtext_auto()
# 定义您的本地字体路径
my_font_path <- "Data/AlibabaPuHuiTi-2-55-Regular.ttf"
my_font_name <- "Alibaba"
# 注册字体
if (file.exists(my_font_path)) {
font_add(my_font_name, regular = my_font_path)
base_font_family <- my_font_name
message(paste("成功加载本地字体:", my_font_path))
} else {
warning(paste("未找到字体文件:", my_font_path, ",尝试使用系统默认字体。"))
tryCatch({
font_add("Arial", "arial.ttf")
base_font_family <- "Arial"
}, error = function(e) {
base_font_family <- "sans"
})
}
# ---- Step 3: 读取地理数据 ----
tryCatch({
cities_data <- st_read("China Map/中国_市.geojson", quiet = TRUE)
districts_data <- st_read("China Map/中国_县.geojson", quiet = TRUE)
message("GeoJSON 地图文件读取成功。")
}, error = function(e) {
stop("读取 GeoJSON 失败,请检查 'China Map' 文件夹。错误: ", e$message)
})
# ---- Step 4: 定义目标区域 ----
target_areas_cities_cn <- c("成都市", "绵阳市", "宜宾市", "德阳市", "南充市", "达州市",
"泸州市", "乐山市", "自贡市", "眉山市", "遂宁市", "内江市",
"广安市", "雅安市", "资阳市")
target_areas_districts_cn <- c("渝北区", "渝中区", "九龙坡区", "沙坪坝区", "南岸区", "江津区",
"北碚区", "巴南区", "涪陵区", "璧山区", "万州区", "永川区",
"长寿区", "合川区", "大渡口区", "铜梁区", "大足区", "綦江区",
"荣昌区", "开州区", "潼南区", "梁平区", "南川区", "云阳县",
"忠县", "垫江县", "黔江区", "丰都县", "石柱土家族自治县",
"彭水苗族土家族自治县", "武隆区", "城口县",
"秀山土家族苗族自治县", "酉阳土家族苗族自治县", "江北区")
gb_code_for_jiangbei <- '156500105'
# ---- Step 5: 筛选与清洗数据 ----
sichuan_cities <- cities_data %>%
filter(name %in% target_areas_cities_cn) %>%
mutate(name = trimws(name))
chongqing_districts <- districts_data %>%
filter((name %in% target_areas_districts_cn & name != "江北区") |
(name == "江北区" & gb == gb_code_for_jiangbei)) %>%
mutate(name = trimws(name))
sichuan_chongqing <- rbind(sichuan_cities, chongqing_districts) %>%
distinct(name, .keep_all = TRUE)
# ---- Step 6: 读取 Excel 指标数据 ----
excel_path <- "Output.bk/分类指标社会网络分析结果.xlsx"
node_data_for_plot <- NULL
if (file.exists(excel_path)) {
tryCatch({
node_data <- read_excel(excel_path, sheet = "Node_Data")
if (all(c("Node", "度中心性") %in% names(node_data))) {
node_data_for_plot <- node_data %>%
select(Node, `度中心性`) %>%
rename(name = Node, value_to_plot = `度中心性`) %>%
mutate(name = trimws(name), value_to_plot = as.numeric(value_to_plot)) %>%
filter(!is.na(value_to_plot))
message("Excel 指标数据读取成功。")
}
}, error = function(e) { warning("Excel读取出错: ", e$message) })
}
# ---- Step 7: 合并数据 ----
if (!is.null(node_data_for_plot)) {
sichuan_chongqing <- sichuan_chongqing %>% left_join(node_data_for_plot, by = "name")
} else {
sichuan_chongqing$value_to_plot <- NA
}
# ---- Step 8: 计算中心点并处理标签 (包含忠县特定修复) ----
sichuan_chongqing_centroids <- suppressWarnings(st_point_on_surface(sichuan_chongqing))
chongqing_core_cn <- c("江北区", "沙坪坝区", "九龙坡区", "渝中区", "大渡口区", "南岸区")
chongqing_core_labels <- c("1", "2", "3", "4", "5", "6")
core_mapping <- setNames(chongqing_core_labels, chongqing_core_cn)
sichuan_chongqing_centroids <- sichuan_chongqing_centroids %>%
mutate(
# 1. 核心区转数字
label = ifelse(name %in% chongqing_core_cn, core_mapping[name], name),
# 2. 通用简化规则 (成都市 -> 成都, 忠县 -> 忠)
label = ifelse(label %in% chongqing_core_labels, label, {
temp <- label
temp <- gsub("土家族|苗族|自治县", "", temp)
temp <- gsub("[市区县]$", "", temp)
temp
}),
# 3. 【特定修复】如果原名是"忠县",强制改为"忠县" (覆盖掉上面的通用规则)
label = ifelse(name == "忠县", "忠县", label)
)
message("标签处理完成 (忠县已单独修正)。")
# ---- Step 9: 计算共享边界 ----
shared_boundary <- NULL
tryCatch({
sc_proj <- st_transform(st_make_valid(sichuan_cities), 3857)
cq_proj <- st_transform(st_make_valid(chongqing_districts), 3857)
sc_bound <- st_boundary(st_union(sc_proj))
cq_bound <- st_boundary(st_union(cq_proj))
shared_proj <- st_intersection(sc_bound, cq_bound)
if (!st_is_empty(shared_proj)) {
shared_boundary <- st_transform(shared_proj, 4326)
}
}, error = function(e) { warning("共享边界计算失败: ", e$message) })
# ---- Step 10: 坐标转换 ----
target_plot_crs <- 4326
sichuan_chongqing <- st_transform(sichuan_chongqing, target_plot_crs)
sichuan_chongqing_centroids <- st_transform(sichuan_chongqing_centroids, target_plot_crs)
# ---- Step 11: 绘图 ----
annotation_text <- "1: 江北 2: 沙坪坝 3: 九龙坡\n4: 渝中 5: 大渡口 6: 南岸"
annotation_grob <- textGrob(
label = annotation_text,
hjust = 0.5, vjust = 0.5,
gp = gpar(fontsize = 8, fontfamily = base_font_family, lineheight = 1.3)
)
map_plot <- ggplot() +
# 底图
geom_sf(data = sichuan_chongqing, aes(fill = value_to_plot),
color = "gray60", linewidth = 0.2) +
# 共享边界
{ if (!is.null(shared_boundary))
geom_sf(data = shared_boundary, color = "black", linewidth = 0.8)
} +
# 标签
geom_sf_text(data = sichuan_chongqing_centroids, aes(label = label),
size = 2.8, color = "black", family = base_font_family,
check_overlap = FALSE) +
# 指北针
annotation_north_arrow(location = "tl", which_north = "true",
pad_x = unit(0.3, "cm"), pad_y = unit(0.5, "cm"),
height = unit(1.2, "cm"), width = unit(1.2, "cm"),
style = north_arrow_fancy_orienteering) +
# 比例尺
annotation_scale(location = "bl", width_hint = 0.25,
pad_x = unit(0.5, "cm"), pad_y = unit(0.5, "cm"),
text_family = base_font_family) +
# 颜色条
scale_fill_gradient(name = "度中心性",
low = "#FDE7D7", high = "#F08B5D",
na.value = "white",
guide = guide_colorbar(direction = "horizontal",
title.position = "top",
barwidth = unit(10, "lines"),
barheight = unit(0.6, "lines"))) +
# 核心区说明
annotation_custom(
grob = annotation_grob,
xmin = 106.5, xmax = 109,
ymin = 27.5, ymax = 28.0
) +
# 主题
theme_minimal(base_family = base_font_family) +
theme(
axis.title = element_blank(),
axis.text = element_text(color = "black", size = 8, family = base_font_family),
panel.grid.major = element_line(color = "grey90", linetype = "dashed"),
legend.position = c(0.75, 0.12),
legend.background = element_blank(),
legend.title = element_text(size = 9, face = "bold", family = base_font_family),
plot.margin = unit(c(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5), "cm")
) +
# 坐标系
coord_sf(crs = target_plot_crs, clip = "off")
# ---- Step 12: 输出 ----
print(map_plot)
'''



